Galvanizing (용융 아연도금)
The galvanizing process consists of three basic steps: surface preparation, galvanizing and inspection.
Surface Preparation is the most important step in the application of any coating. In most instances where a coating fails before the end of its expected service life, it is due to incorrect or inadequate surface preparation.
The surface preparation step in the galvanizing process has its own built-in means of quality control in that zinc simply will not react with a steel surface that is not perfectly clean. Any failures or inadequacies in surface preparation will be immediately apparent when the steel is withdrawn from the molten zinc. Any areas that were not properly prepared will remain uncoated. Immediate corrective action is taken.
Surface preparation for galvanizing typically consists of three steps: caustic cleaning, acid pickling and fluxing.
Caustic(가성) Cleaning – A hot alkali solution often is used to remove organic contaminants such as dirt, paint markings, grease and oil from the metal surface. Epoxies, vinyls, asphalt or welding slag must be removed before galvanizing by grit-blasting, sandblasting or other mechanical means.
Pickling – Scale and rust normally are removed from the steel surface by pickling in a dilute solution of hot sulfuric acid or ambient temperature hydrochloric acid.
Fluxing – Fluxing removes oxides(산화물) and prevents further oxides from forming on the surface of the metal prior to galvanizing and promotes bonding of the zinc to the steel or iron surface. The method for applying the flux depends upon whether the particular galvanizing plant uses the wet or dry galvanizing process.
In the dry galvanizing process, the steel or iron materials are dipped or pre-fluxed in an aqueous solution of zinc ammonium chloride. The material is then thoroughly dried prior to immersion in molten zinc.
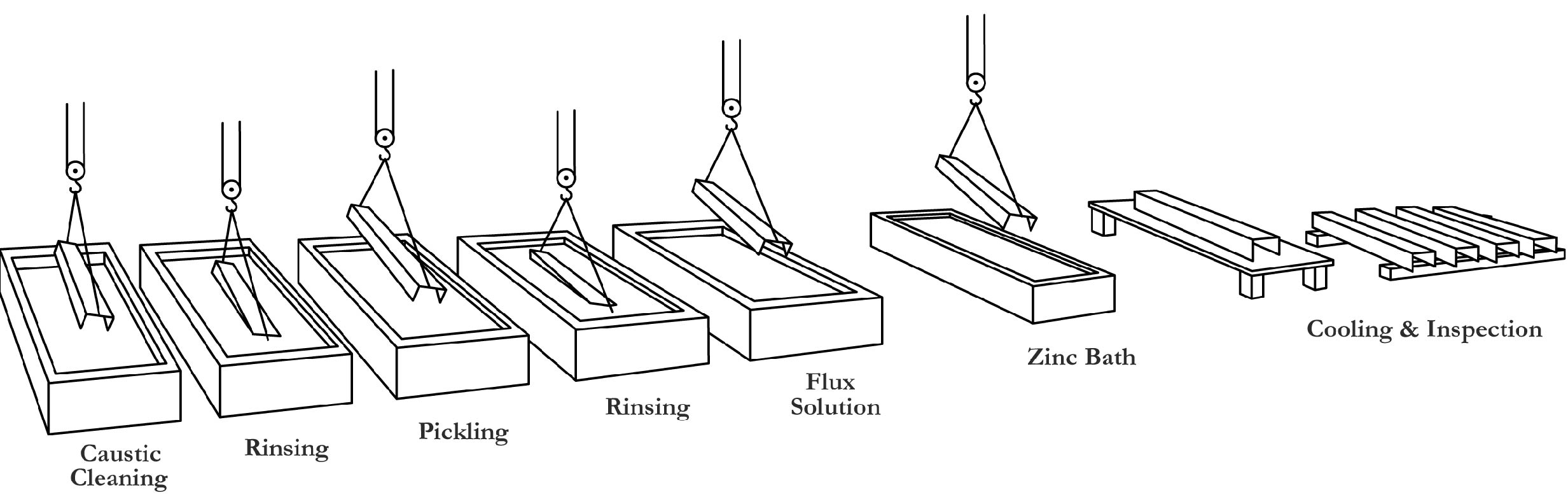
In this step, the material is completely immersed(담궈지다) in a bath consisting of a minimum 98% pure molten zinc. The bath chemistry is specified by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) in Specification B 6. The bath temperature is maintained at about 850 F (454 C).
Fabricated items are immersed in the bath long enough to reach bath temperature. The articles are withdrawn slowly from the galvanizing bath and the excess zinc is removed by draining, vibrating and/or centrifuging.
The chemical reactions that result in the formation and structure of the galvanized coating continue after the articles are withdrawn from the bath as long as these articles are near the bath temperature. The articles are cooled in either water or ambient(주변의) air immediately after withdrawal from the bath.
The two properties of the hot-dip galvanized coating that are closely scrutinized after galvanizing are coating thickness and coating appearance. A variety of simple physical and laboratory tests may be performed to determine thickness, uniformity, adherence and appearance.
Products are galvanized according to long-established, well-accepted and approved standards of the ASTM, the Canadian Standards Association (CSA), and the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO). These standards cover everything from the minimum required coating thicknesses for various categories of galvanized items to the composition of the zinc metal used in the process.
출처: http://www.highwaysafety.net/oldsite/Galvanizing/galvanizing.html
용융 아연도금
[ Zinc Hot Dip Galvanizings, Hot Dip Galvanizing ]
아연은 융점이 약 420℃로, 가격이 싸며, 철강의 방식도금으로써 효과가 크며, 경제적이기 때문에 용융도금의 수요가 많다. 도금공정은, 탈지 세정→산세→플럭스 처리→건조→용융 아연욕 침적→수냉→건조이다. 예를 들어, 철근에 도금을 할 경우, 욕 온도 460±5℃, 침적 시간은 약 1분간으로 500~1500g/㎥의 아연 부착량이 된다. 일반적인 아연도금의 두께는 아연철판에서 8~20㎛, 관이나 구조물에서 75~125㎛이다. KS D 8308「용융 아연도금」, D 9521「용융 아연도금 작업표준」, D 0201「용용 아연도금 시험방법」에 규정되어 있다.
[네이버 지식백과] 용융 아연도금 [Zinc Hot Dip Galvanizings, Hot Dip Galvanizing] (도금기술 용어사전, 2000.6, 도서출판 노드미디어)